Introduction
Property binding (one-way binding) in Angular allows us to bind the property of an element to a target property. The DOM property is the target property. We assign values to the target property.
Examples
Injecting a Website’s Link and Title
In the app.component.ts file we type the following inside the AppComponent Class:
public url: string = "https://www.google.com";
public site: string = "Google";
and in the app.component.html file, type the following:
<a [href]="url">{{site}}</a>
We get the following result:

NOTE: If the value of the variable that is placed between the text interpolator Angular {{}} contains Javascript code for example, Angular will not process it, but will output it in raw format. However, Angular can sanitize the value of a variable before displaying it in the frontend using [innerHTML] (e.g. [innerHTML]="someValue") , [href], style({}). For more information, check out Angular’s documentation on Sanitization and security contexts.
Disabling a Button
Another way that property binding can be used is in disabling a button.
In the app.component.ts file, we add the following code inside the AppComponent class:
public disableButton: boolean = true;
and in our app.component.html file, type the following code:
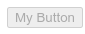
<button [disabled]=disableButton>My Button</button>
Our button is now disabled
Using Property Binding to Style a Button
Let’s style the button from our previous example:
In app.component.ts file add the following line of code inside the AppComponent class:
public buttonClass: string = "button";
and in the app.component.html file, replace the [disabled]=disableButton with the following:
<button [ngClass]="buttonClass">My Button</button>
Finally, add the following CSS class to the app.component.css file:
.button {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
};
The button should look like this:
